Describe the Changes in Arteries That Occur With Atherosclerosis
In arteriosclerosis the walls of the arteries become thick and stiff and hypertension results. The aorta is affected earliest followed by the.

What Is Atherosclerosis New Beginnings Health Care Integrative Medical Center
At onset there are usually no symptoms but if they develop symptoms generally begin around middle age.
. As the blood pressure rises caused by the general narrowing of the arteries forcing the heart to pump harder the bulge in the aneurism silently increases in size. The plaque forms in the arteries over many years in a process called atherosclerosis. This reduces the supply of oxygen-rich blood to tissues of vital organs in the body.
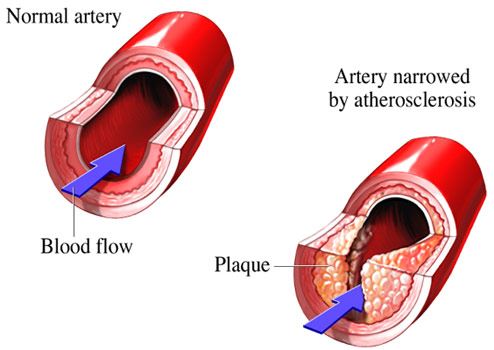
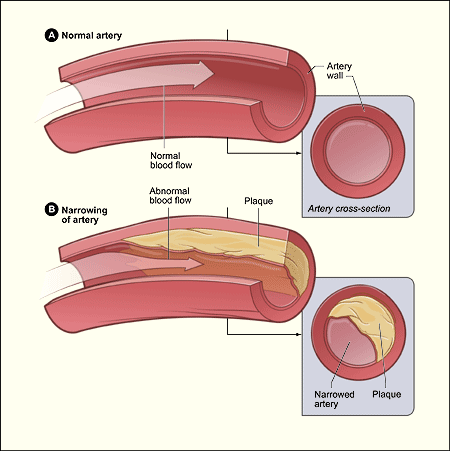
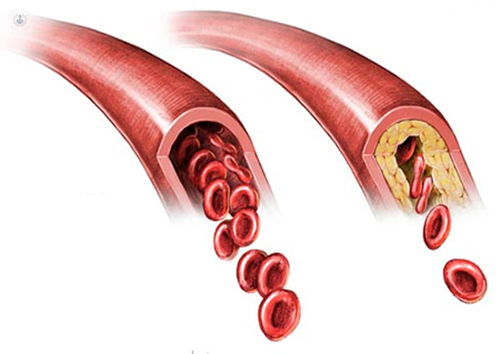
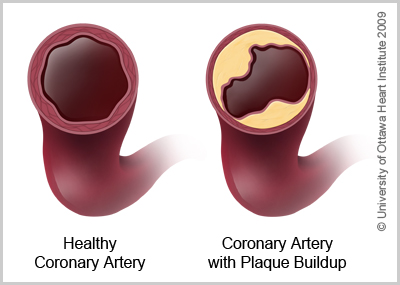
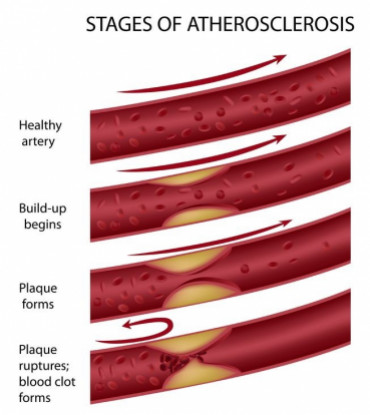
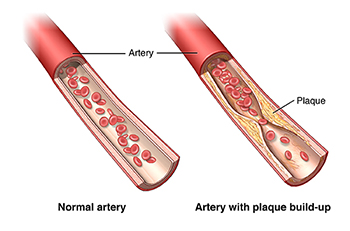
These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. Normal artery and an artery with plaque buildup. When the plaque builds up it causes your arteries to narrow.
In atherosclerosis which is the most common form of arteriosclerosis small patchy areas called atheromas form that can. Plaque fatty deposits build up in your arteries is called atherosclerosis. It concentrates on the histogenesis of intimal hyperplasia and describes the histologic changes that occur in a vein graft after its insertion.
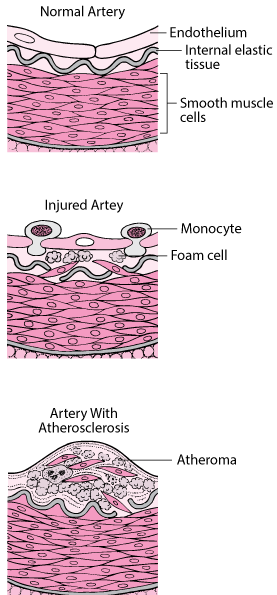
It all begins with inflammation and atherosclerosis of the aorta for example. Activated endothelial cells attract. The response to injury hypothesis explains atherosclerotic plaque development as a chronic inflammatory response resulting from injury to the endothelial lining of the artery.
2 - Myocardial infarction or heart attack. The initial lesions are usually caused by the focal increase in the lipoproteins of the intimal layer of the arteries. Over the years cholesterol and cells become plaque in the wall of your artery.
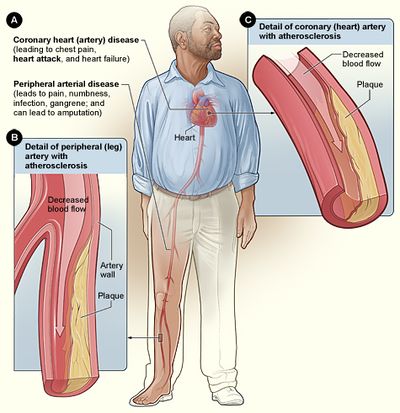
Chronic endothelial injury see risk factors that contribute to endothelial damage which results in endothelial dysfunction. The fatty deposits cause arteries to narrow which restricts blood flow to tissues. The buildup of plaques can restrict blood flow through the arteries causing disease in various parts of the body including the heart and brain.
Plaque creates a bump on your artery wall. As plaque builds up the wall of the blood vessel thickens. Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease characterized by the accumulation of lipids and fibrous elements in the large arteries.
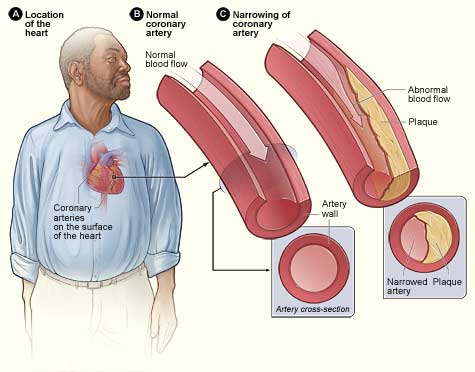
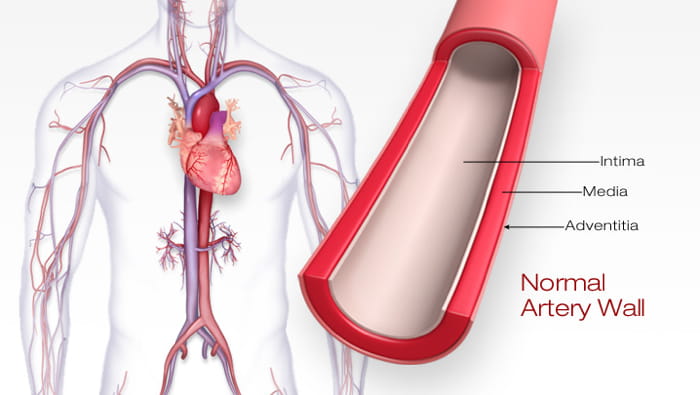
The anatomy of a normal artery is shown in Fig. Sclerosis refers to loss of elasticity or hardening of the artery. Over time the plaques harden narrow the opening of the arteries and restrict the blood flow.
Atherosclerosis is a form of arteriosclerosis hardening of the arteries. Atherosclerosis is a complex disorder that refers to the hardening of the arteries due to the accumulation of lipids particularly cholesterol. Atherosclerosis thickening or hardening of the arteries.
Atherosclerosis is a disease characterized by the development of plaques fatty deposits in arteries. An atheroma is a deteriorated thickened area on the inner lining of a large or medium-sized artery. Atherosclerosis increases the risk of heart attack and stroke.
1 - Coronary artery thrombosis. Atherosclerosis arteriosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a potentially serious condition where arteries become clogged with fatty substances called plaques or atheroma. Plaque is made up of deposits of fatty substances cholesterol cellular waste products calcium and fibrin.
Also pieces of the plaque fall of the wall of the arteries and travel in the blood stream where it can eventually block the flow of blood. In nearly every case of atherosclerosis the. Your white blood cells stream in to digest the LDL.
Clinically this stage can be manifested by. As the final treatment for atherosclerotic disease is not established yet however action is need in preventing the disease onset. Answer Atherosclerosis occurs in elastic and muscular arteries and may occur iatrogenically in vein grafts interposed in the arterial circulation.
This can cause pain in muscles especially when exercising as the muscles cant get enough blood and therefore not enough nutrients to function properly. Injury to the endothelial cell of the artery resulting in endothelial cell dysfunction is the first step in the process. 3 - Cerebro-vascular stroke.
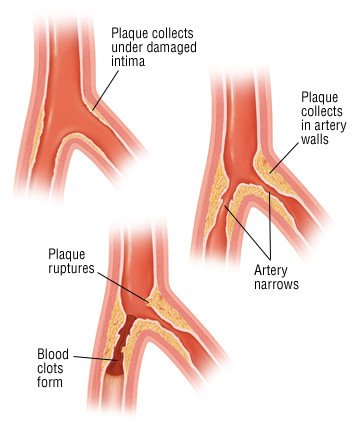
This narrows the channel within the artery reducing blood flow. It describes the build-up of plaques also known as fatty deposits in the inside of arteries that cause the disorder to be progressive as it can either block the artery or increase the chance of an artery being blocked. The development of arterial atherosclerosis may occur when deposits of cholesterol and plaque accumulate at a tear in the inner lining of an artery.
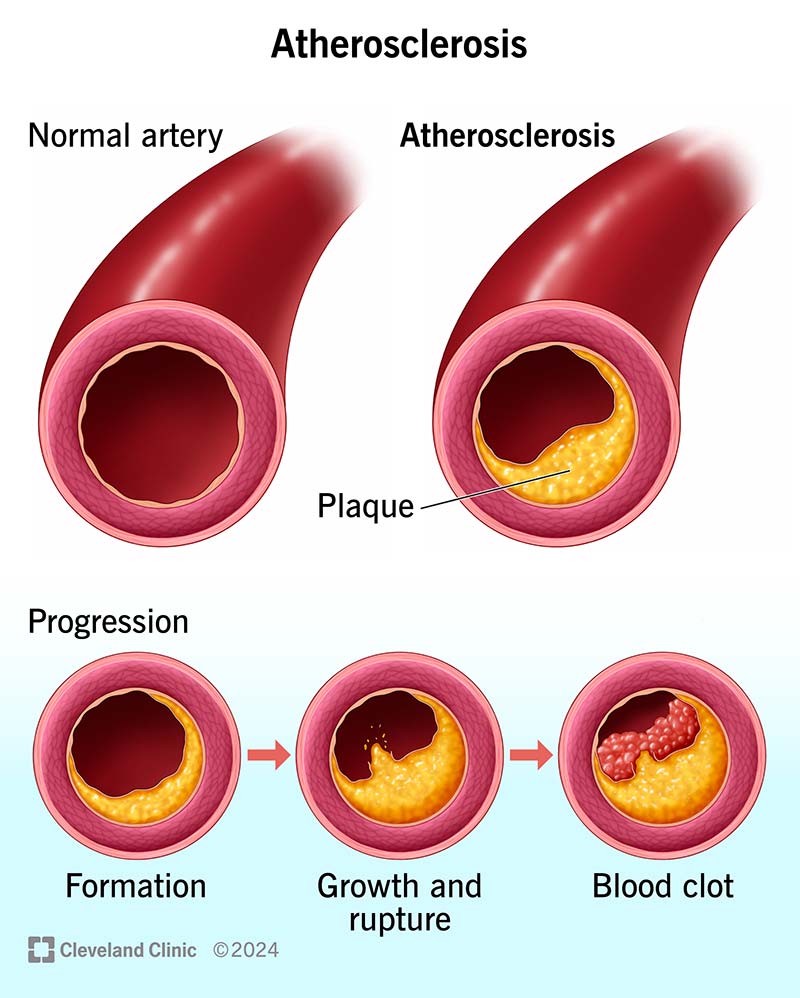
The atherosclerosis process Fatty streaks formation Atheroma formation Atherosclerotic plaques formation. Atherosclerosis is a type of arteriosclerosis in which fatty deposits called plaques build up in the arteries. Atherosclerosis develops slowly as cholesterol fat blood cells and other substances in your blood form plaque.
As the deposits harden and occlude the arterial lumen blood flow to distant tissues decreases and a clot may become lodged completely blocking the artery. As it builds up in the arteries the artery walls become thickened and stiff. It is caused by a buildup of plaque in the inner lining of an artery.
This process of arterial stiffening is called arteriosclerosis. Fatty streaks formation Both animal and human studies show that the fatty streaks are the first sign of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis It is a disease in which plaques that are made up of fat cholesterol calcium and other substances build up in the walls of arteries the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart throughout the body.
The early lesions of atherosclerosis consist of subendothelial accumulations of cholesterol-engorged macrophages called foam cells. This article reviews the success of vein-to-artery grafts and the published data on patency rates and the major causes for graft failure ie intimal hyperplasia and atherosclerosis. Aneurisms are silent and deadly.
Other diseases that can cause change in arterial structure are called. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis involves a complex series of events similar to a chronic inflammatory process with the formation of atherosclerotic plaque as the end result. These deposits are made up of cholesterol fatty substances cellular waste products calcium and fibrin a clotting material in the blood.
The plaque hardens in the passageways of the arteries which supply Oxygen rich blood to the major organs. Describe the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. Breaking the cholesterol-related chains of.
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities called lesions.

Causes Of Coronary Artery Disease
Atherosclerosis Guide Causes Symptoms And Treatment Options

Atherosclerosis Heart And Stroke Foundation
Vascular Endovascular Surgery Atherosclerosis
In Depth Reports Coronary Artery Disease
Atherosclerosis North Texas Vascular Center
Atherosclerosis Heart And Blood Vessel Disorders Merck Manuals Consumer Version

Atherosclerosis Pathology Britannica
Atherosclerosis What Is It Symptoms And Treatment Top Doctors
Atherosclerosis Causes Symptoms Risks Tests
Pacific Heart Lung Blood Institute Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery Disease Atherosclerosis Ottawa Heart Institute
/GettyImages-1148113699-f84eaf35c56d44b6bc1bde6d62f3a29e.jpg)
What Causes Plaque In The Arteries
Atherosclerosis Health Navigator Nz

Comments
Post a Comment